Lazydocker is an open-source terminal user interface (TUI) that simplifies the process of managing Docker containers and related resources. Designed with developers in mind, it offers a visual way to interact with Docker without having to memorize complex command-line instructions. Instead of typing long strings of CLI commands, you can navigate through your Docker environment with an intuitive interface.
With Lazydocker, developers and system administrators can monitor, control, and optimize their Docker environments efficiently. It provides clear visibility into container performance, simplifies log inspection, and enables the management of images, volumes, and networks—all from a single terminal window.
To explore more about Lazydocker, visit the official website: https://lazydocker.com/.
Managing Containers with Lazydocker
View Running and Stopped Containers
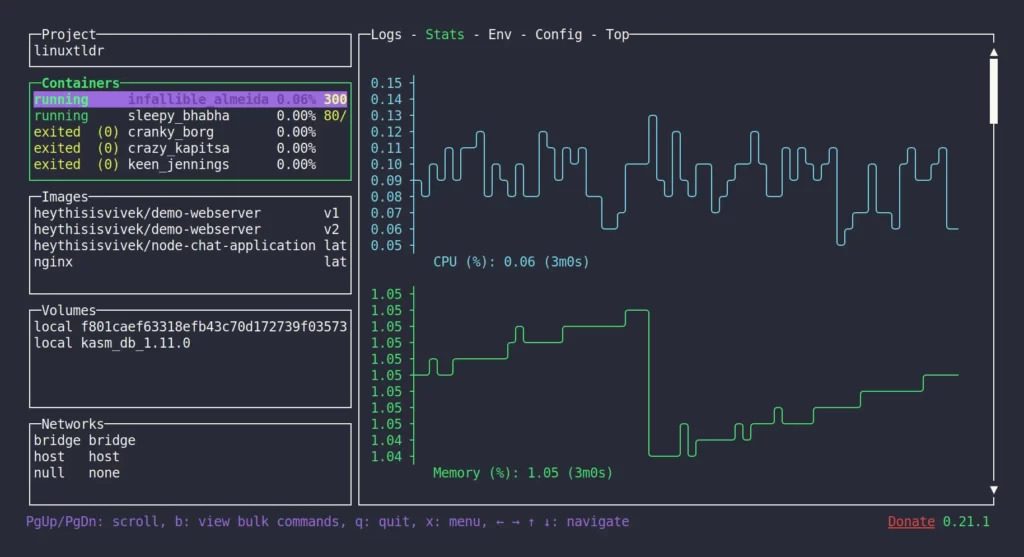
Lazydocker displays both active (running) and inactive (stopped) containers in an organized list. Each entry includes key metadata such as container name, status, uptime, and image source. This provides a comprehensive overview of your Docker environment at a glance.
Inspect Container Details and Logs
One of Lazydocker’s most powerful features is the ability to inspect detailed logs and metadata for each container. By selecting a container, you can:
- View real-time stdout/stderr logs
- Examine container configuration and environment variables
- Check mount points and exposed ports
- This reduces the need to run multiple docker commands and improves debugging workflows.
Start, Stop, Restart, Pause, and Remove Containers
Basic container lifecycle operations are made simple:
- Start a stopped container with a single keystroke.
- Stop or restart a running container effortlessly.
- Pause and resume containers without disrupting data.
- Remove containers cleanly when they are no longer needed.
- This allows users to perform container management actions quickly and intuitively.
View Resource Usage Stats (CPU, Memory)
Lazydocker integrates container resource monitoring. Each container’s CPU and memory usage is displayed live, helping you identify bottlenecks or runaway processes. This visibility is essential for performance tuning and capacity planning.
Benefits of Container Management in Lazydocker
Managing containers in Lazydocker improves efficiency, enhances visibility, and speeds up development and debugging. Developers can focus more on building applications and less on infrastructure management. The interface promotes quicker decisions and better resource optimization.
Managing Docker Images with Lazydocker
View All Images Available on the Host
Lazydocker lists all Docker images available on your system. Each image shows details such as repository, tag, image ID, and size. This simplifies inventory tracking, especially in environments with many custom images.
Remove Unused or Dangling Images
Keeping your Docker environment clean is vital for performance and storage. Lazydocker allows users to:
- Identify dangling images (unnamed or untagged)
- Remove obsolete or unused images
- Reclaim disk space quickly
- These actions are just a few clicks away within the Lazydocker interface.
Inspect Image Details such as Tags and Sizes
With Lazydocker, users can drill down into each image to view specific tags, image creation date, layer sizes, and more. This helps in version control, debugging build issues, and managing registry resources effectively.
How Image Management Improves System Cleanliness
Effective image management leads to:
- Reduced disk usage
- Faster system performance
- Better clarity in container image inventory
- Lazydocker’s visual representation encourages regular cleanup and better image hygiene.
- Managing Docker Volumes with Lazydocker
List Volumes Used by Containers
Docker volumes are crucial for persistent data. Lazydocker lists all volumes along with information on:
- Mount points
- Associated containers
- Usage status
- This helps identify which volumes are active and which are safe to delete.
Inspect Volume Details
By selecting a volume, users can view:
- Volume name and driver
- Mount location on the host
- Containers using the volume
- This level of detail is vital for debugging data issues and managing persistent storage.
Remove Unused Volumes
Unused volumes can quickly accumulate and consume disk space. Lazydocker simplifies their removal by allowing you to:
- Identify orphaned volumes
- Delete them with confirmation
- This process keeps your Docker environment lean and efficient.
Importance of Managing Storage Effectively
Proper volume management prevents:
- Disk space exhaustion
- Data redundancy
- Orphaned storage lingering after container removal
- Lazydocker makes this routine maintenance quick and user-friendly.
Managing Docker Networks with Lazydocker
View Existing Docker Networks
Lazydocker presents a complete list of available Docker networks. This includes default networks (like bridge, host, and none) and any custom networks you’ve defined for container communication.
Inspect Network Configurations
For each network, Lazydocker displays:
- Network name and driver
- Connected containers
- Subnet and gateway info
- Network scope
- This visibility helps troubleshoot connectivity and isolation issues between services.
Remove Unused Networks
Just like with volumes and images, Lazydocker makes it easy to identify and remove unused or redundant networks. This minimizes clutter and avoids configuration conflicts.
How Network Management Supports Container Communication
Proper Docker network management is key to:
- Enabling secure communication between services
- Controlling access boundaries
- Preventing misconfigurations
- With Lazydocker, network setup and troubleshooting become less error-prone and more intuitive.
Managing Docker Compose Projects with Lazydocker
Overview of Docker Compose Integration
Lazydocker has built-in support for Docker Compose, making it easy to manage multi-container applications. Whether you’re running a development stack or a microservices cluster, Compose support is a major productivity boost.
Start, Stop, and Restart Compose Services
Within Lazydocker, users can:
- Start an entire Compose project
- Stop all services with a single command
- Restart specific services selectively
- This removes the need to switch between CLI and docker-compose.yml files.
View Compose Project Logs and Status
Lazydocker aggregates logs from all services within a Compose project. This centralized logging makes it easier to:
- Debug startup issues
- Monitor service health
- Identify error patterns
- Service status (up, down, paused) is also clearly displayed.
Benefits of Visual Compose Management
Using Lazydocker to manage Docker Compose projects allows teams to:
- Reduce operational overhead
- Get fast feedback during development
- Maintain better control over service orchestration
- It brings a simplified, interactive experience to an otherwise script-heavy process.
Conclusion
Lazydocker transforms the way developers and sysadmins interact with Docker. By offering a visual interface within the terminal, it reduces the learning curve, speeds up workflows, and enhances visibility across all critical Docker components.
With Lazydocker, you can manage:
- Docker containers (run, stop, inspect, monitor)
- Docker images (inspect, delete, clean up)
- Volumes (view, inspect, remove)
- Networks (view, configure, troubleshoot)
- Docker Compose projects (start, stop, monitor)
This unified interface improves efficiency, helps prevent errors, and ensures that your Docker environment stays clean and organized.